Mechanical, electrical, and plumbing
M: The mechanical design elements of a building, most especially the heating and cooling systems, help make life inside more comfortable. These systems allow us to occupy buildings in hot and cold temperatures, under all weather conditions.
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING / HVAC ENGINEERING
• Heating, Ventilating, and Air Conditioning Systems
• Central Plant Design
• Exhaust Systems
• Direct Digital Control (DDC) Systems
• Chilled Water Systems
• Heating Water Systems
E: The electrical system in a building keeps the lights on, keeps our devices powered , and keeps the other systems running. Architectural lighting design and plans are a crucial component of the electrical engineering process.
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
• Comprehensive Electrical System Design
• Onsite Power Generation Requirements and Distribution
• Critical Power Systems
• Integration of IT and AV Into Overall Building Design
• Device Coordination and Arc Fault Services
• Lightning Protection Systems
PLUMBING ENGINEERING
• Domestic Cold and Hot Water Systems
• Domestic Waste and Vent Systems
• Fuel Gas Piping Systems
• Storm Water Systems
• Performance Specification of Automatic Sprinkler Systems
• Water Conservation Systems
Ducts Types
1- Rectangular or Square ductwork commonly is fabricated to suit by specialized metal shops. For ease of handling, it most often comes in 2 sections (or joints).
2- Round duct is made using forming machines which can make round duct in nearly any diameter.
Duct Material
Galvanized or hot-dipped galvanized steel (GI) it is the standard and most common material used in fabricating ductwork because Its corrosion-resistance, strength and relatively inexpensive cost.by avoids cost of painting.
Zinc offers protection to the steel by forming a barrier against the elements, as well as sacrificing itself to prevent steel corrosion.
The amount of zinc coating applied over top the core steel for corrosion protection varies depending upon end-use and specification requirements, and can be controlled and measured to industry standards.
Common coating weights for galvanized steel are G30, G40, G60 and G90. It is important to note that. These coating weights designate a total of 0.30, 0.40, 0.60, and 0.90 oz/ft2, respectively. While these. The corrosion resistance, and thus, the service life, is proportionate to the amount of zinc coating on the steel. Hence, the service life of a G90 will generally be 3 times that of a G30 and 1.5 times that of a G60 in the same environment. However, the service life of any galvanized steel product is dependent upon the environment in which it is exposed.
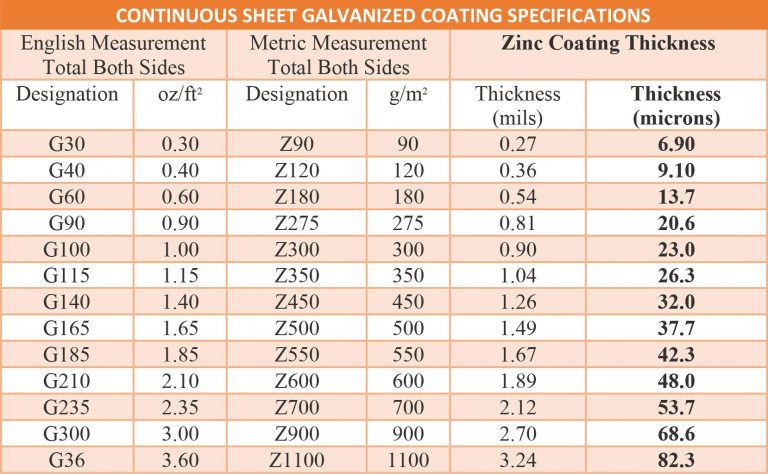
Grade:
DX51D + Z275MA-C (DIN EN 10346 and DIN EN 10143)
Sheet thickness
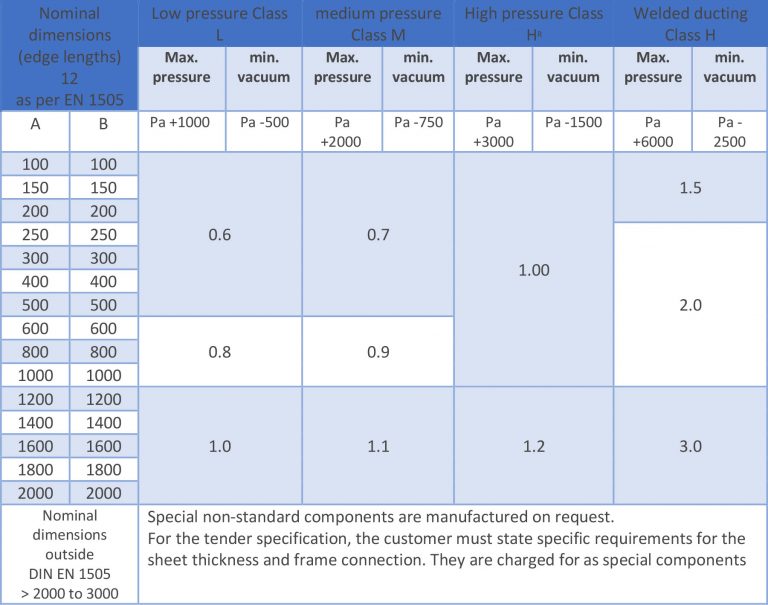
Ducts and fittings are fabricated from galvanized sheets which are hemmed and seamed, pressure-welded, or riveted. The ducts and fittings are available in low, medium and high pressure versions (max. overpressure / min. vacuum):
class L design (low-pressure design):
standard design from -400 Pa to +1000 Pa
class M design (medium-pressure design):
from -1000 Pa to 2000 Pa
class HR design (High-pressure design):
from -1500 Pa to 3000 Pa
class H design (High-pressure design):
from -2500 Pa to 6000 Pa
See below The table provides Sheet thicknesses and pressure ratings as per VDI 3803.
Combined Air Handling Unit
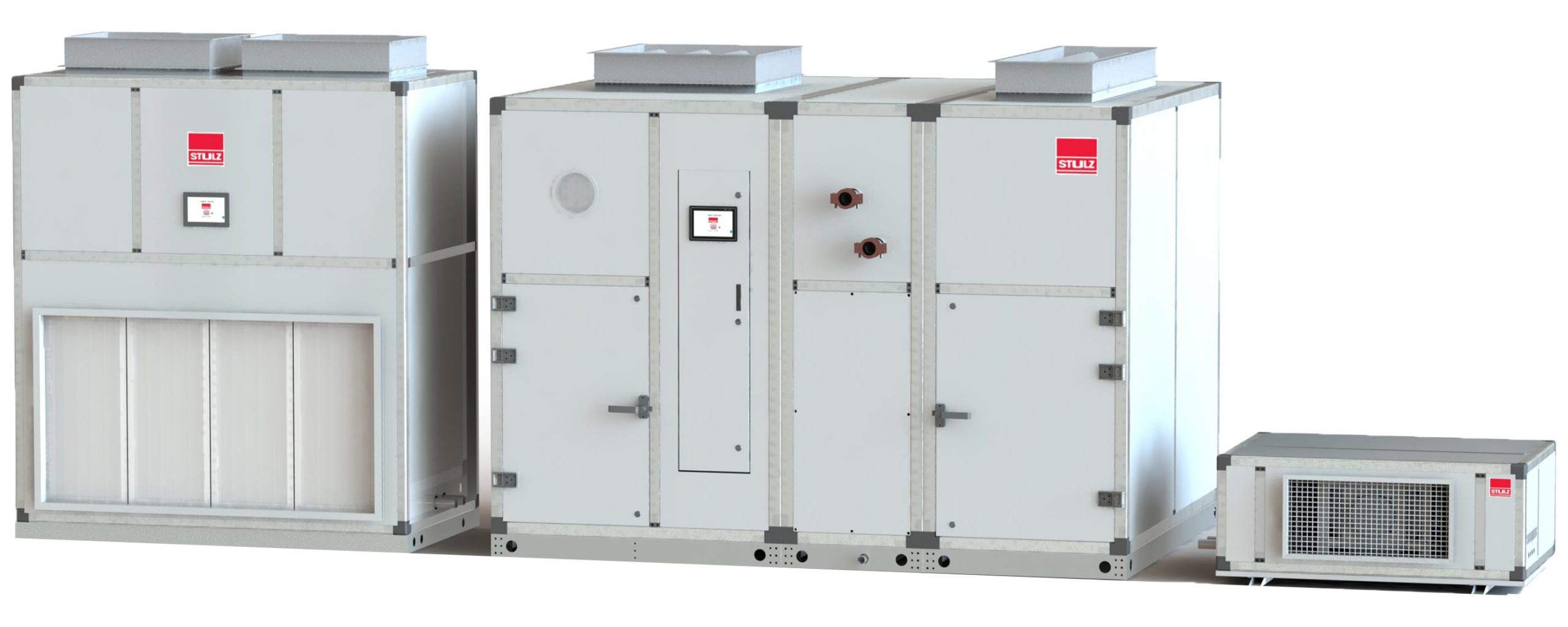

The shell of the combined air handling unit is made of two-layer color steel plate which is filled with polyurethane foam or polystyrene. The frame is made of special steel or aluminum alloy. The sealing performance between shell and frame is great, so limited air could leak from the seam. Copper pipe coved by aluminum corrugated fin is adopted for the heat exchanger, making the heat transfer coefficient very high.
As an air conditioner component, our combined air handling unit can be divided into several sections: blowing-in section, heat exchanging section, humidifying section, steam heating section, middle efficiency filtering section, mixing section, energy recovery section, and air returning section. Besides, the structure could be customized according to clients’ requirements.
Feature of different sections
Mixing section
In this section. the return air will be mixed with fresh air. Unless specified, this section comes with an access door, but the air flow valve is not included.
Air flow control section
The air flow control section of the combined air handling unit can adjust the air flow of the air conditioning system. Actually, it is the combination of the air extraction section and air returning section (or fresh air section). If there is no specific statement, this section does not include air flow valves for all of these subsections. However, there is an air flow control valve for the entire air flow control section, and an access door is available for this section.
Energy recovery section
A certain amount of energy of the exhaust will be transferred to fresh air in the energy recovery section. The recovery rate could be higher than 70%. Thus the power consumption is greatly reduced.
Heat exchanging and water retaining section
The temperature and humidity of the air will be reduced in this section. To heat the temperature, you can use warm water below 65°C. The water tray and condensed water outlet pipe are available at the bottom of this unit. A water retaining board is needed when the face velocity is above 2.5m/s.
