Air-cooled chillers
Chillers that used air for cooling the condensing unit, this type does not use a cooling tower.
Water-cooled chillers:
Chillers that used water for cooling the condensing unit, this type use a cooling tower.
Cooling tower:
The cooling tower is usually located up on the roof.
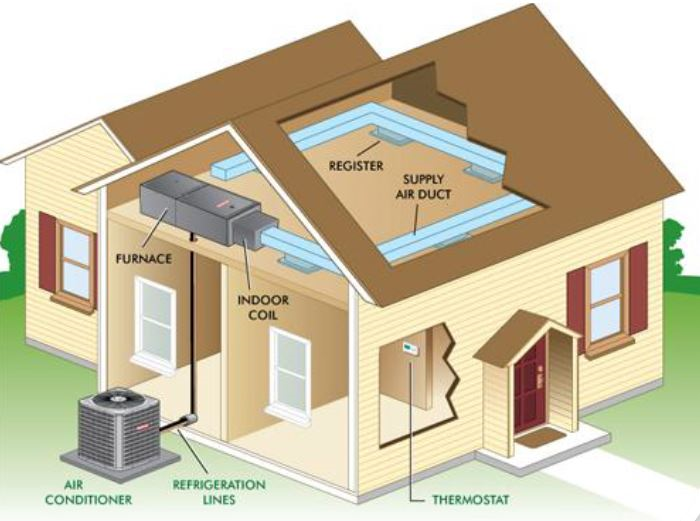
Direct expansion system (dx):
In the direct expansion or DX types of air central conditioning plants, the air used for cooling space is directly chilled by the refrigerant in the cooling coil of the air handling unit. Since the air is cooled directly by the refrigerant the cooling efficiency of the DX plants is higher. However, it is not always feasible to carry the refrigerant piping to the large distances hence, direct expansion or the DX type of central air conditioning system is usually used for cooling the small buildings or the rooms on the single floor.
The direct expansion system in HVAC has been growing rapidly due to its ability to get rid of most ductwork and piping. The popularity of this system is because the installation work has been made easier hence reducing the cost of the overall system.
The DX System works in such a way that the evaporator is located in the space to be refrigerated. When the refrigerant in the evaporator coil expanded, it will cool the space by absorbing the heat from it. The mini-splits, window air conditioners, and packaged units are examples of such systems.
Advantages of Direct Expansion System
Low installation costs.
– Ease to test, adjust, and balance the system.
– Minimum ceiling or wall space needed.
– Low energy consumption.
– Low maintenance costs.
– The individual section can be operated without running the entire system in the building.
– Comfort under varying load conditions.
– Low noise level (NC 35).
– Good relative humidity control.